Learning Objectives:
- Learn about IoT Sensor types and applications
- Learn how to incorporate IoT Sensors into a solution
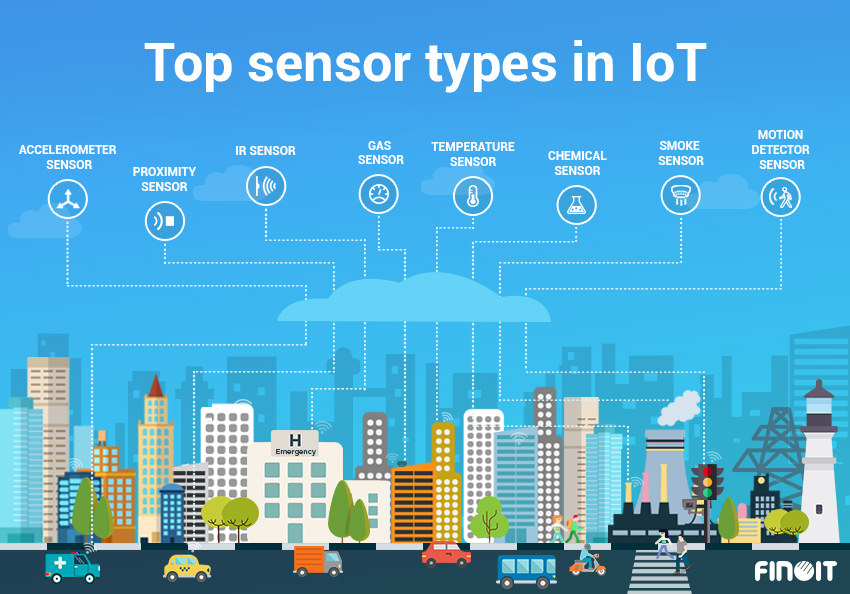
IoT sensors are electronic devices that are designed to detect and measure physical phenomena, such as temperature, humidity, pressure, motion, light, and sound, and transmit the collected data to other devices or systems via the internet. They are the essential component of the IoT ecosystem, as they enable the monitoring and control of physical environments and processes.

IoT sensors come in various shapes and sizes and measure a variety of parameters, such as temperature, humidity, pressure, motion, light, sound, and countless more. They can be installed in homes, factories, hospitals, farms and nature reserves to collect data and enable real-time analysis and decision-making. The concept of smart-cities is a prime example of the potential employment potential of these systems to increase urban efficiency, decrease costs, and produce higher standards of living.
These aforementioned sensors utilize different types of connectivity technologies to transmit data, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LTE/5G, and LoRaWAN. They can be powered by batteries or wired connections, and they can operate independently or as part of a larger IoT system. Systems can be contained and optimized for both small areas and larger coordinated geolocations.
The systems built can lead to the creation of numerous applications, such as smart home automation, industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, environmental monitoring, and smart cities. They are rapidly evolving in both niche and cross-platform areas, and new types of sensors and technologies are emerging frequently, strengthening the core of these systems.
Sensors can be incorporated into a LoRaWAN network using a LoRaWAN gateway, which acts as a bridge between the sensor devices and the cloud-based application that processes and stores the sensor data.
Here are the general steps to incorporate IoT sensors into a LoRaWAN network:
- Choose an IoT sensor that is compatible with the LoRaWAN protocol. There are many types of sensors that can be used, and so choosing the best for your specific situation is the pivotal first step. Be sure to thoroughly evaluate the system fit, the size, and other factors that must be addressed prior to deployment.
- Install the IoT sensor in the desired location and ensure that it is properly configured to communicate with the LoRaWAN gateway.
- Install a LoRaWAN gateway, or map the existing gateway, in the area where the IoT sensors will be deployed. The gateway acts as a bridge between the sensors and the cloud-based application. The gateway receives the data from the sensors, and then sends it to the cloud-based application.
- Configure the LoRaWAN gateway to connect to the appropriate LoRaWAN network server. The LoRaWAN network server manages the communication between the gateway and the cloud-based application.
- Configure the cloud-based application to receive and process the sensor data. This may involve setting up a dashboard to view the data in real-time, or configuring an alert system to notify users of any abnormal sensor readings.
Once the above steps have been completed, the sensors will be incorporated into the LoRaWAN network and the sensor data will be available for analysis and use in various applications.
