Learning Objectives:
- Recognize a step-by-step outline of the DIY process
- Get a feel for the project management skills needed to see out an idea
- Realize the important distinction between initiation, testing, deployment, and monitoring phases

Here is a general overview of the potential DIY process that is associated in the deployment an IoT application:
- Define Your Application: The first step is to define your IoT application, including the problem you are trying to solve and the data you need to collect. You should consider what hardware and software you will need to implement your solution.
- Choose Your IoT Platform: Once you have defined your application, you need to choose an IoT platform that can support your system’s needs. Consider factors such as data storage, analytics, and security when choosing your platform.
- Select Your Hardware: Next, you need to select the hardware that will collect and transmit your data. This may include sensors, gateways, and other devices. Make sure the hardware you choose is compatible with your IoT platform.
- Build Your IoT Network: With your hardware selected, you need to build your IoT network. This may involve setting up gateways, configuring devices, and ensuring that all hardware is connected to your IoT platform. Or onboarding to an existing IoT network such as Helium.
- Develop Your Application: Once your hardware and network are in place, you can start developing your IoT application. This may involve programming in languages such as Python or JavaScript, depending on your platform.
- Test and Validate Your Application: Once your application is developed, you need to test and validate it to ensure that it is working properly. This may involve testing your hardware and network, as well as analyzing data to ensure that it meets your requirements. This is a good stage to seek external feedback, if you’re deploying an enterprise solution, you may want to hone in on your platform’s ease-of-use.
- Deploy Your Application: Once you have tested and validated your application, you can deploy it in the field. This may involve installing hardware and configuring devices in the environment where they will be used.
- Monitor and Maintain Your Application: After deployment, you need to monitor and maintain your IoT application to ensure that it continues to function properly. This may involve monitoring data quality, troubleshooting issues, providing updates and performing maintenance on hardware and software as needed.
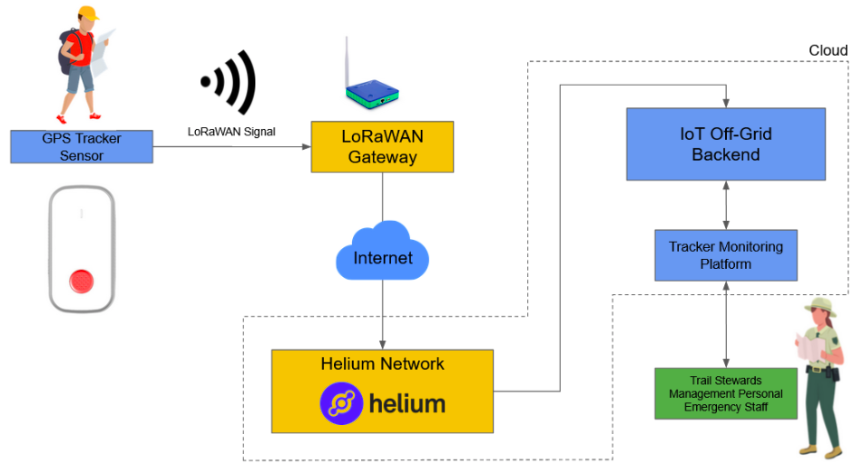
From Sensor to End User.
